NCLEX Memory Hints: PPE

NCLEX Memory Hints: Personal Protective Equipment
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is used any time there is risk of contamination. In facilities, there are guidelines for each type of situation and the PPE that is required. Much of this is determined by the CDC and other infectious disease organizations.
Gloves are required for any contact with body secretions and excretions.
Gowns are required for a bath or any type of activity where you will lean over the patient and contact might occur with body fluids.
Goggles are required any time there is a risk of splashing.

Scenarios
Consider these two scenarios and what type of PPE you would wear? (Based on the textbook.)

Textbook answers
- For both scenarios, you should have chosen gloves (which I am sure you did ).
- When changing an incontinent patient, there is risk of contamination to your clothing, and a gown should be worn, in addition to the gloves.
- When emptying a urinary catheter, there is a...
NCLEX Memory Hints: Anemia and Hydration

NCLEX Memory Hints: Anemia and Hydration
The CBC with differential is a frequently ordered lab test and provides much information regarding infection, anemia, coagulation, and hydration. When bone marrow suppression occurs, low levels of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets will be seen.
Monitoring anemia
Anemia is seen frequently in many different types of patients. When the red blood cells are low, pallor will be seen. If the red blood cells are too numerous, such as in polycythemia vera, the blood is “thicker” and there is a risk for blood clotting and myocardial dysfunction due to the strain.
Men have a higher red blood cell count mostly due to hormonal differences which stimulate higher hemoglobin production and greater muscle mass. For ease in clinical practice, it is helpful to remember the normal level for hemoglobin for everyone is 12-18 g/dL. Using the memory hint below, the normal RBC and hematocrit levels are easy to remember.
...
NCLEX Memory Hints: Leukemia

NCLEX Memory Hints: Leukemia
Leukemia is a group of blood cancers that usually begin in the bone marrow and results in overproduction of immature white blood cells. Symptoms may include bleeding and bruising, bone pain, fatigue, fever, enlarged lymph nodes, and an increased risk of infections. Diagnosis is typically made by blood tests and confirmed by bone marrow biopsy. Lab values include a high white blood cell count, but they are immature. Red blood cells and platelets are reduced by the cancerous process. Blast cells will be seen on diagnosis and if an acute crisis has occurred during or after treatment.
Leukemia is the most cause of cancer in children and teens and can be acute or chronic. Both chronic types of leukemia are seen more in adults. It will be lymphocytic or myelocytic.

Acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL)
ALL is seen primarily in kids (“The little guys”) and accounts for 80% of childhood leukemia. Treatment is with chemotherapy. Remission can occur...
NCLEX Memory Hints: Legal Terms and Concepts

NCLEX Memory Hints: Legal Terms and Concepts
There are multiple legal terms and concepts to be aware of for the NCLEX exam. A select few include the Board of Nursing, professional responsibilities, malpractice insurance, Good Samaritan Law, and torts.
Torts are wrongful acts that are committed against a person or a property. Select unintentional and intentional torts are covered.

Unintentional torts
Unintentional torts include negligence which is not acting as a prudent nurse and acting below the acceptable standard of care. Negligence includes commission which is doing something wrong (e.g., operating on the wrong body part). It also includes omission which is failing to do something.
Intentional Torts
Assault and battery
Assault and battery are frequently interchanged. Assault is when a patient is fearful. Battery is violence in the form of touching or contact with a patient. As example of battery is starting an IV on a competent patient who is refusing the procedure.

...
NCLEX Memory Hints: Radiation

NCLEX Memory Hints: Radiation
Radiation therapy may external or internal depending on the type of cancer that is being treated. Medical professionals need to use radiation precautions when unsealed radiation is used.
External radiation
External radiation is also known as teletherapy. It is done Monday through Friday for 15-30 minutes a day at a center. After 5 days, fatigue is a major side effect. Patients need the two-day period to rest and strengthen their immune system. The patient will not be radioactive after a treatment. Tissue damage to the target area may be seen. Radiation pneumonia may develop with chest radiation.

Internal radiation
Internal radiation is also known as brachytherapy. The radiation dose is concentrated in the tumor and may be temporary or a permanent implant. It may also be sealed or unsealed. As an example, prostate cancer may be treated with temporary or permanent internal radiation.
Temporary (in prostate cancer)
Temporary-hollow...
NCLEX Memory Hints: Crutches

NCLEX Memory Hints: Crutches
Crutches are frequently dispensed in the outpatient setting and education is important for patient safety and to prevent complications.
The height of the crutches should measure 2-3 finger widths below the anterior axillary fold to avoid brachial plexus injury and causing weakness of the forearm.
The handgrip should be placed to allow the angle of elbow flexion to be 30 degrees to avoid nerve injury and the hand will be numb.

Patients should place the crutches 6-10 inches in front and to the side of the patient’s toes, depending on body size, to provide a wide base of support.
If patients will need to climb stairs, education should include going up the stairs and going down.
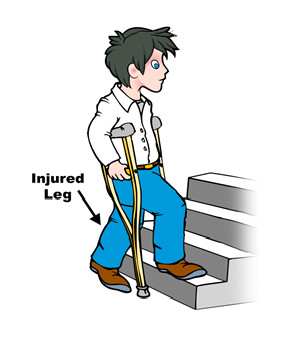
To go up, good leg first, bad leg and crutches follow.
To go down, bad leg and crutches first, good leg follows.

Are you prepared for the Next Generation NCLEX?
Click Here To Get Started
BrainyNurses.com by Educational Concepts,...
NCLEX Memory Hint: Renal Dysfunction

Lab Values: Renal Dysfunction
There is a broad range of dysfunction which can occur with the kidneys. Renal insufficiency is frequently seen in the elderly and in those with hypertension and is evidenced by a glomerular filtration rate (GFR) of < 30%. Renal failure can be acute, chronic, or end stage. End-stage is a GFR of < 15% and dialysis is required to live. There are numerous causes of chronic renal failure including diabetes and hypertension. While these conditions cause renal failure, renal failure also leads to diabetes because of the insulin resistance that develops, and it also leads to hypertension.
Renal insufficiency
In renal insufficiency, the kidneys lose the ability to hold onto sodium and water. Thus, urine output is increased. ACE inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers will be started to preserve renal function. If the GFR falls, these drugs will be stopped due to associated hyperkalemia in the presence of renal dysfunction. The urine will...
NCLEX Memory Hints: Skin Lesions

Dermatology is a challenging field because of all the different types of lesions and conditions which may develop. Often, a biopsy is needed for a definitive diagnosis. Repeated sun exposure is a risk factor for actinic keratosis and basal and squamous cell cancer.
Nevi
One of the most common growths which can be present at birth or develop over the lifetime. They can become dysplastic and have atypical features and growth pattern between the spectrum of a benign mole to melanoma but not be cancerous. Dysplastic moles can be removed with laser.
Seborrheic keratosis
Benign skin growth that originates in the keratinocytes. They tend to be darker in color and occur later in life and may be mistaken for cancerous lesions. Treatment is local incision.
Actinic keratosis
Precancerous lesions which present as a yellow or brown scale, primarily on sun exposed area and increase with aging. They are surgically removed or may be treated by freezing the area.
 Basal cell
Basal cell
Type of cancer...

